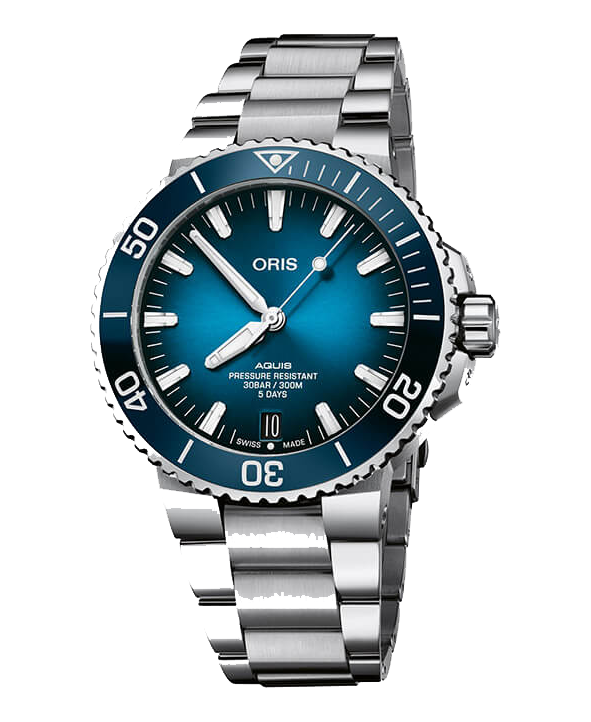
PHOTO: Warming of sea surface in Asia-Pacific. Redder areas indicate a higher increase in temperature. (Photo credit: Delfino, R.J. et al. Response of damaging Philippines tropical cyclones to a warming climate using the pseudo global warming approach. Clim Dyn 61 (2023): p. 3506.).
The Philippines should brace for potentially stronger and more destructive typhoons due to climate change, warns new research coming out of the University of the Philippines – Diliman College of Science’s Institute of Environmental Science and Meteorology (UPD-CS IESM).
Dr. Rafaela Jane Delfino and Dr. Gerry Bagtasa, together with colleagues from the UK, found that future Philippine typhoons may have a higher cyclone damage potential (CDP) than today’s typhoons.
CDP is a metric that takes into account several factors, including the size of the cyclone and the speed of its winds. The scientists gathered data from recent typhoons and projected these onto likely future climate scenarios to figure out future CDPs. The greater the CDP, the greater potential damage costs, particularly from winds.
Specifically, the researchers looked at three of the most deadly super typhoons in recent history: Haiyan (which happened in 2013 and was locally named Yolanda); Bopha (2012, Pablo); and Mangkhut (2018, Ompong). They then hypothesized the potential damage from these typhoons if they happened in a future where the climate is forecast to be warmer and more humid, based on multiple climate projections for the years 2070 to 2099.
Moreover, by employing various projections and considering several factors such as atmospheric temperature, sea surface temperature, pressure, and relative humidity, the researchers were able to conclusively link climate change to the intensification of the three Philippine typhoons mentioned in the study. They also found that future typhoons may be expected to be stronger and more damaging. Like spinning tops, the potentially faster winds and slower movement of these future typhoons could lead to them lingering longer over land and therefore causing more damage.
For example, under one forecast model, the CDP from a future cyclone similar to Super Typhoon Yolanda was seen to be as much as 37% greater than the damage experienced in 2013. In another simulation, Super Typhoon Ompong, which had a simulated maximum wind speed of 205 kph under present climate conditions, could potentially hit 270 kph under future climate conditions. The projections also showed an increase of as much as 50 kph in the maximum wind speeds of future typhoons like Yolanda and Pablo.
“Based on our simulations, it is found that the most damaging tropical cyclones like Haiyan, Bopha, and Mangkhut will have higher wind-related damage potential in the future,” the researchers concluded in their paper.
“Tropical cyclones of such intensity and damage potential in the future will have serious implications with the increasing exposure and vulnerability in the Philippines,” they added, calling for further research using other models and typhoon data sets.